Kết quả 1 đến 1 của 1
-
08-30-2023, 11:51 AM #1
 Silver member
Silver member
- Ngày tham gia
- Jul 2023
- Bài viết
- 132
Can Diabetics Eat Coconut? A Comprehensive Guide
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose, a type of sugar that provides energy for cells. People with diabetes either do not produce enough insulin, a hormone that helps glucose enter the cells, or are resistant to its effects. This causes high blood glucose levels, which can lead to various complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision loss.
Coconut is a tropical fruit that has many health benefits. It is rich in fiber, antioxidants, minerals, and medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are a type of fat that can help lower cholesterol and improve blood sugar control. Coconut can be consumed in different forms, such as fresh, dried, shredded, milk, oil, water, and flour.
But can diabetics eat coconut? The answer is yes, but with some caution and moderation. Here are some pros and cons of eating coconut for people with diabetes, and some tips on how to incorporate it into a balanced diet.Pros of Eating Coconut for Diabetics[/b]
- Coconut fiber can help lower the glycemic index (GI) of foods, which is a measure of how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, which can prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar. Coconut also contains resistant starch, which is a type of carbohydrate that is not digested by the body and acts like fiber.
- Coconut MCTs can help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, which means that the body can use glucose more efficiently and lower blood sugar levels. MCTs can also increase the production of ketones, which are an alternative fuel source for the brain and muscles when glucose is scarce. This can help prevent ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition that occurs when the body produces too many ketones due to lack of insulin.
- Coconut antioxidants can help protect the cells from oxidative stress, which is a state of imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage the cells and cause inflammation, which can worsen diabetes complications. Antioxidants are substances that can neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
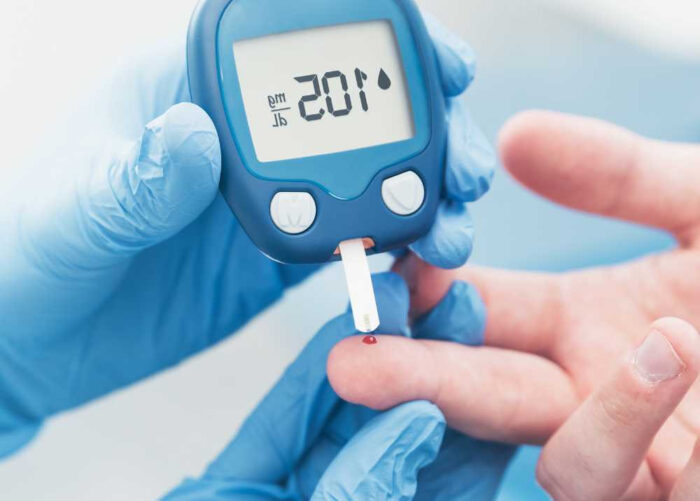
- Coconut minerals such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus can help regulate blood pressure, nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone health. These minerals are especially important for people with diabetes who are at risk of hypertension, neuropathy, muscle cramps, and osteoporosis.Cons of Eating Coconut for Diabetics[/b]
- Coconut is high in calories and saturated fat, which can contribute to weight gain and high cholesterol if consumed in excess. Weight gain and high cholesterol are risk factors for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death among people with diabetes. Therefore, it is important to limit the intake of coconut products that are high in fat and calories, such as oil, milk, cream, and butter.
- Coconut water contains natural sugars that can raise blood sugar levels if consumed in large amounts. Although coconut water has a lower GI than regular soft drinks and juices, it still has about 6 grams of sugar per 100 ml. Therefore, it is advisable to drink coconut water in moderation and check blood sugar levels before and after drinking it.
- Coconut flour is made from dried and ground coconut meat that has most of the fat removed. It is gluten-free and high in fiber and protein, which makes it a good alternative for wheat flour for people with diabetes who have celiac disease or gluten intolerance. However, coconut flour is also very dense and absorbent, which means that it requires more liquid and eggs to make baked goods. This can increase the calorie and fat content of the final product.How to Eat Coconut for Diabetics[/b]
- Choose fresh or dried coconut over processed products that may have added sugar or preservatives.
- Use coconut oil sparingly as a cooking oil or a salad dressing. A tablespoon of coconut oil has about 120 calories and 14 grams of saturated fat.
- Use coconut milk or cream as a substitute for dairy products in soups, curries, smoothies, or desserts. Look for unsweetened varieties that have less than 10 grams of sugar per 100 ml.
- Can coconut water go bad spoil if consumed occasionally as a treat or post-workout rehydration beverage? Restrict your consumption to one cup (240 ml) a day, and monitor your blood sugar levels before and after consumption.
- Use coconut flour as a substitute for wheat flour in baking or pancakes. Follow the recipe instructions carefully and adjust the amount of liquid and eggs accordingly. A quarter cup (30 grams) of coconut flour has about 120 calories and 4 grams of fiber.
- Eat other foods that are good for diabetics along with coconut products. These include lean protein sources such as fish, chicken, eggs, beans, nuts, seeds; whole grains such as oats, quinoa, brown rice; fruits such as berries, apples, oranges; vegetables such as leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes; and healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, flaxseeds.The Bottom Line[/b]
Coconut is a nutritious and delicious fruit that can be enjoyed by people with diabetes in moderation. It has many health benefits, such as lowering blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, and providing antioxidants and minerals. However, it also has some drawbacks, such as being high in calories and saturated fat, and containing natural sugars that can affect blood sugar levels. Therefore, it is important to choose the right type and amount of coconut products, and balance them with other foods that are good for diabetics. By doing so, you can reap the benefits of coconut without compromising your health.
Source: https://thanhcongcraft.com/how-to-make-a-coconut-bowl-a-step-by-step-guideView more random threads:
- Đồng hồ tranh treo tường - Cách làm mới không gian sống độc đáo
- Mẫu Tủ Bếp Gỗ Tự Nhiên Giá Tốt Và Rẻ Nhất 2017 Tại Vũng Tàu
- Tấm tăng tiện nghi đệm khách sạn nào uy tín hiện nay?
- chọn mẫu bàn học sinh đẹp phù hợp với không gian
- Top các model bếp giovani tốt nhất hiện giờ (p2)
- Thiết Kế Mẫu Biệt Thự Tân Cổ Điển Sang Trọng
- Các mua thảm lót 3D cho phòng ngủ
- sử dụng điều hòa thế nào là tốt nhất
- chọn ghế hợp với phòng khách ở thành phố
- hướng dẫn lưu lại sàn gỗ công nghiệp ngoài trời đúng cách
Các Chủ đề tương tự
-
Crafting Elegance: Premier Coconut Bowl Manufacturers
Bởi Thanhcongcraft trong diễn đàn Nội Ngoại ThấtTrả lời: 0Bài viết cuối: 08-12-2023, 09:28 AM -
Using Coconut Shell: Harnessing the Potential of Coconut Shells
Bởi Thanhcongcraft trong diễn đàn Nội Ngoại ThấtTrả lời: 0Bài viết cuối: 08-09-2023, 04:19 PM -
Are Coconut Bowls Healthy? Coconut shell bowl benefits
Bởi Thanhcongcraft trong diễn đàn Nội Ngoại ThấtTrả lời: 0Bài viết cuối: 08-09-2023, 03:49 PM -
How to fix cracked coconut bowl?
Bởi Thanhcongcraft trong diễn đàn Nội Ngoại ThấtTrả lời: 0Bài viết cuối: 08-08-2023, 02:16 PM -
Uses of Coconut Husk and Coconut Fibre
Bởi Thanhcongcraft trong diễn đàn Nội Ngoại ThấtTrả lời: 0Bài viết cuối: 07-21-2023, 03:10 PM



 Trả lời kèm Trích dẫn
Trả lời kèm Trích dẫn





Mô đun giám sát Mayr Roba Việt Nam
Hôm qua, 09:47 PM in Rao vặt tổng hợp